ATHLETE's FOOT
Athlete's foot is a very common skin condition that affects the sole of the foot and the skin between the toes. It is usually a scaly, red, itchy eruption and occasionally may be weepy and oozing. It affects the feet of athletes and nonathletes alike. Although it is frequently caused by a fungal infection, other causes may be indistinguishable without proper testing.
The medical name for athlete's foot caused by a fungus is tinea pedis. There are a variety of fungi that cause athlete's foot, and these can be contracted in many locations, including gyms, locker rooms, swimming pools, nail salons, and from contaminated socks and clothing. The fungi can also be spread directly from person to person by contact. Most people acquire fungus on the feet from walking barefoot in areas where someone else with athlete's foot has walked. Some people are simply more prone to this condition while others seem relatively resistant to it. Another colorful name for this condition is "jungle rot," often used by members of the armed services serving in tropical climates.
Without the proper environment (warmth and moisture), the fungus may not easily infect the skin. Up to 70% of the population may develop athlete's foot at some time. An infection by athlete's foot fungi does not confer any resistance to subsequent infections.
CAUSE:-Athlete's foot is most commonly caused by the fungi Trichophyton rubrum or T. mentagrophytes,but may also be caused by Epidermophyton floccosum. Most cases of athlete's foot in the general population are caused by T. rubrum; however, the majority of athlete's foot cases in athletes are caused by T. mentagrophytes.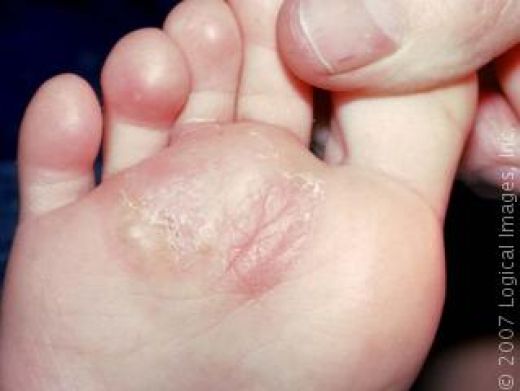
What does athlete's foot look like?
Most cases of athlete's foot are barely noticeable with just slightly dry, flaky skin. More extensive athlete's foot may look like red, peeling, dry skin areas on one or both soles of the feet. Sometimes the dry flakes may spread onto the sides and tops of the feet. Most commonly, the rash is localized to just the bottoms of the feet. The space between the fourth and fifth toes also may have some moisture, peeling, and dry flakes.
There are three common types of fungal athlete's foot:
(1) soles of the feet, also called "moccasin" type;
(2) between the toes, also called "interdigital" type; and
(3) inflammatory type or blistering.
Occasionally, it may appear as small or large blisters of the feet (called bullous tinea pedis), thick patches of dry, red skin, or calluses with redness. Sometimes, it may look like just mild dry skin without any redness or inflammation.
Fungal athlete's foot may present as a rash on one or both feet and even involve the hand. A "two feet and one hand" presentation is a very common presentation of athlete's foot, especially in men. Hand fungal infections are called tinea manuum. Fungal athlete's foot may also be seen along with ringworm of the groin (especially in men) or hand(s). It is helpful to examine the feet whenever there is a fungal groin rash called tinea cruris. It is important to treat all areas of fungal infection at one time to avoid reinfection. Simply treating the soles and ignoring the concurrent fungal infection of toenails may result in recurrences of athlete's foot.
Treatments
Without medication, athlete's foot resolves in 30–40% of cases and topical antifungal medication consistently produce much higher percentages of cure. Allylamines such as terbinafine are considered more efficacious than azoles for the treatment of athlete's foot.
Medication
Conventional treatment typically involves daily or twice daily application of a topical medication in conjunction with hygiene measures outlined in the above section on prevention. Keeping feet dry and practicing good hygiene is crucial to preventing reinfection. Severe or prolonged fungal skin infections may require treatment with oral antifungal medication.Zinc oxide-based diaper rash ointment may be used.For temporary/emergency relief from symptoms in the field, after clearing dead skin and thoroughly drying the affected area skin moisturiser should then be applied until thoroughly absorbed to prevent affected skin from drying out and cracking or rubbing and subsequent infection.Excess moisturiser should be wiped off dry and periodically reapplied. Talcum powder can be used to absorb excess environmental moisture to inhibit the infection.
Topical
There are many topical antifungal drugs useful in the treatment of athlete's foot including: miconazole nitrate, clotrimazole, tolnaftate (a synthetic thiocarbamate), terbinafine hydrochloride, butenafine hydrochloride and undecylenic acid. The fungal infection may be treated with topical antifungal agents, which can take the form of a spray, powder, cream, or gel. Topical application of an antifungal cream such as terbinafine once daily for one week or butenafine once daily for two weeks is effective in most cases of athlete's foot and is more effective than application of miconazole or clotrimazole. Plantar-type athlete's foot is more resistant to topical treatments due to the presence of thickened hyperkeratotic skin on the sole of the foot. Keratolytic and humectant medications such as urea, salicyclic acid, and lactic acid are useful adjunct medications and improve penetration of antifungal agents into the thickened skin. Topical glucocorticoids are sometimes prescribed to alleviate inflammation and pruritus associated with the infection.
A solution of 1% potassium permanganate dissolved in hot water is an alternative to antifungal drugs.
Oral
For severe or refractory cases of athlete's foot oral terbinafine is more effective than griseofulvin. Fluconazole or itraconazole may also be taken orally for severe athlete's foot infections. The most commonly reported adverse effect from these medications is gastrointestinal upsetness.

